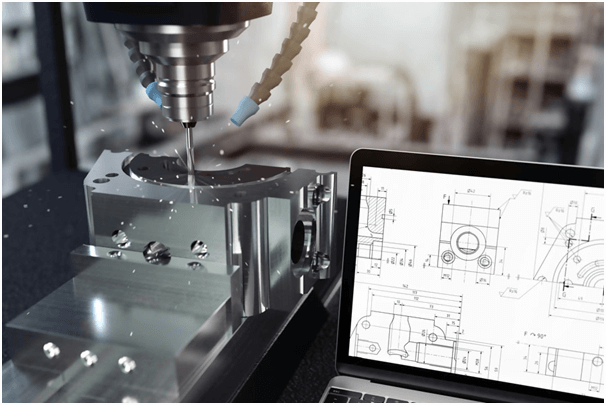
CNC machining is a modern manufacturing procedure whereby a pre-programmed software dictates the movement of factory machinery and tools. The system is used to control sophisticated machineries such as grinders, lathes, routers, and mills. You can learn more about CNC machining to understand how they work. Let’s look at an overview of CNC Machining process.
All to know regarding CNC Machining
Once a CNC system is activated, the required cuts are programed in the software and dictated to corresponding machinery and tools that perform the dimensional tasks as needed.
In the CNC programming process, the code processor in the numerical system will assume flawless mechanism, irrespective of errors. This is good when a CNC machine is dictated to cut in over one direction simultaneously. A sequence of inputs outlines the placement of tools in numerical control platform called part program.
With the numerical control tool, programs are entered through punch cards. By contrast, the CNC machine programs are keyed to the computer via the small keyboard. Note that CNC programming remains in the PC’s memory. The code is prepared and edited by CNC programmers.
So, the CNC platform offers vast computational capacity. The most significant part is that CNC platforms are static because fresh prompts can be included in the pre-existing programs via revised code.

Types of CNC machines
The first numerical control tools were created in the 1940s when motors were first used to control the motion of pre-existing machines. As technology improved, the mechanisms were advanced with analog PCs, and finally with digital PCs that resulted in the growth of CNC machining.
A high number of today’s CNC machines are entirely electronic. Some of the standard CNC run procedures comprise laser cutting, hole punching, and ultrasonic welding. Here are the frequently used tools in CNC platforms:
- CNC mills
CNC mills can run on programs that involve letter and number based prompts that direct pieces across different distances. The programming used for a mill tool is based on G-code or other unique language created by the manufacturing crew. Basic mills comprise of three-axis platform(X, Y, and Z) even though the majority of latest mills can accommodate up to three extra axes.
- Lathes
In lathe tools, indexable machines are used to cut pieces in a circular direction. With CNC systems, the cuts engaged by lathe machines are performed with high velocity and precision. CNC lathes are utilized to generate intricate designs that can’t be done on manually operated versions of the tool. Generally, CNC runs mills’ control functions are the same. As with the first one, lathes are directed by G-code or unique proprietary code. Nevertheless, many CNC lathes have two axes: X & Y.
- Plasma cutters

In plasma cutter machines, materials are cut with a plasma torch. The procedure is mostly applied to metal substances but can be used on other materials. Plasma is created via a combination of electrical arcs and compressed air gas. This helps to generate the heat and speed needed to cut metal.
- Electric discharge machines (EDM)
Also known as die sinking and spark machining, electric-discharge matching is a procedure which molds workpieces into specific shapes via electric sparks. With this process, current discharge happens between tow electrodes, and this eliminates the parts of a particular workpiece.
Once the space within the electrodes reduces, the electric field becomes intense and making it stronger than dielectric. This allows the current to pass within the two electrodes. Thus, portions of workpieces are eliminated by each electrode. Subtypes of electric discharge machining comprise:
- Since EDM, whereby a workpiece and electrode are soaked in dielectric fluid for piece creation.
- Wire EDM, where spark erosion is used to eliminate the parts from conductive materials
Take-Away
In a procedure called flushing, particles from every completed workpiece are eliminated by the liquid dielectric. The liquid appears when the current within two electrodes stop, and it’s designed to get rid of any electric charges.