Looking at the Applications of a DC Machine
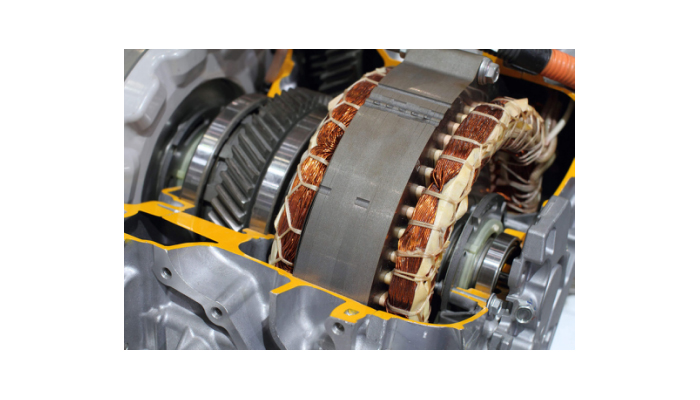

A DC motor refers to a series of a class of different rotary electrical engines that easily convert direct current to mechanical energy, as you have learned in the first blog post of DC contactors. The common types of DC machines solely rely on energy produced using magnetic fields. All kinds of motors in the DC series come with internal mechanisms. They could be electromechanical or better yet electronic. These energies periodically transition their rotational direction into that of the motor. Typically, DC motors were known as the primary forms of motors used mainly since they could easily be powered from an existing direct-current lighting of a power distribution system. In this blog post, you will learn more about DC machines and their applications.
**The Preface **
A DC motor comes with a coil and some running current that generates electromagnetic fields straight at the center of the device’s coil. Typically, in several cases, the magnitude of the field produced using the coil can easily be transformed using the direction it takes, and the total size of the energy that flows through it.
Applications of DC Machines
In the current world, electrical energy is often generated in bulk. That is why there is a rise in the use of DC contactors and machines. Usually, DC generators are limited in the market by nature. They are therefore used in the supply of small to medium ranges of alternators. Some of the industrial applications of these machines include the Electrolytic Processes, Variable speed motor drives, as well as Welding processes.
The Compound Motors
The compound motors are prominently used where there is a need for a high starting torque coupled with constant speed. Some of the examples of the uses of these compound motors include in Shears, Rolling Mills, and Planners, among others.
The small machines of DC come with a fractional rating used as a control device in different Tecno generators, particularly for speed sensing.
The Series DC Motors
These devices are often used in cases where a relatively high starting torque is needed, coupled with additional speed variations. For instance, the series motors herein are commonly used in the Traction systems, Vacuum Cleaning Systems, and Sewing machines.
Shunt DC Motors
The outset of different power electronics has now replaced DC motors in several industrial applications.
Shunt motors are prominently used where there is a need for constant speed during the operation hours of a device. Some of the applications of a DC shunt motor include the operation of a Lathe machine, Conveyors, Weaving Machines, and Spinning machines. The growing demand for products manufactured in these industries has also contributed to the on-going need for shunt motors.
Final Thoughts
There you have it. DC machines and their motors are widely used to power devices from the existing direct-current lighting to various distribution systems. The speed of a DC motor is easily controlled using a stable variable supply voltage, which is reliable in delivering its currents.
Larger DC machines are used in the propulsion of smart vehicles, hoists, as well as drives used in steel rolling mills.